Click to Go Back
Blue Star Tutorial
Click images to enlarge
Click images to enlarge
Step 1 - Query Sequence Submission
BENZ WS accept a single protein sequence in FASTA format with a valid header. Submitted sequence length should range between 40 and 1500 residues.
After query sequence submission, a dedicated job, identified with a unique code, is launched. BENZ WS provides the user with a URL that can be bookmarked to retrieve the results. The waiting page automatically refreshes every 10 seconds. Average running time per query varies between 10 second and 1 minute. Results are stored on the server for at least 7 days.
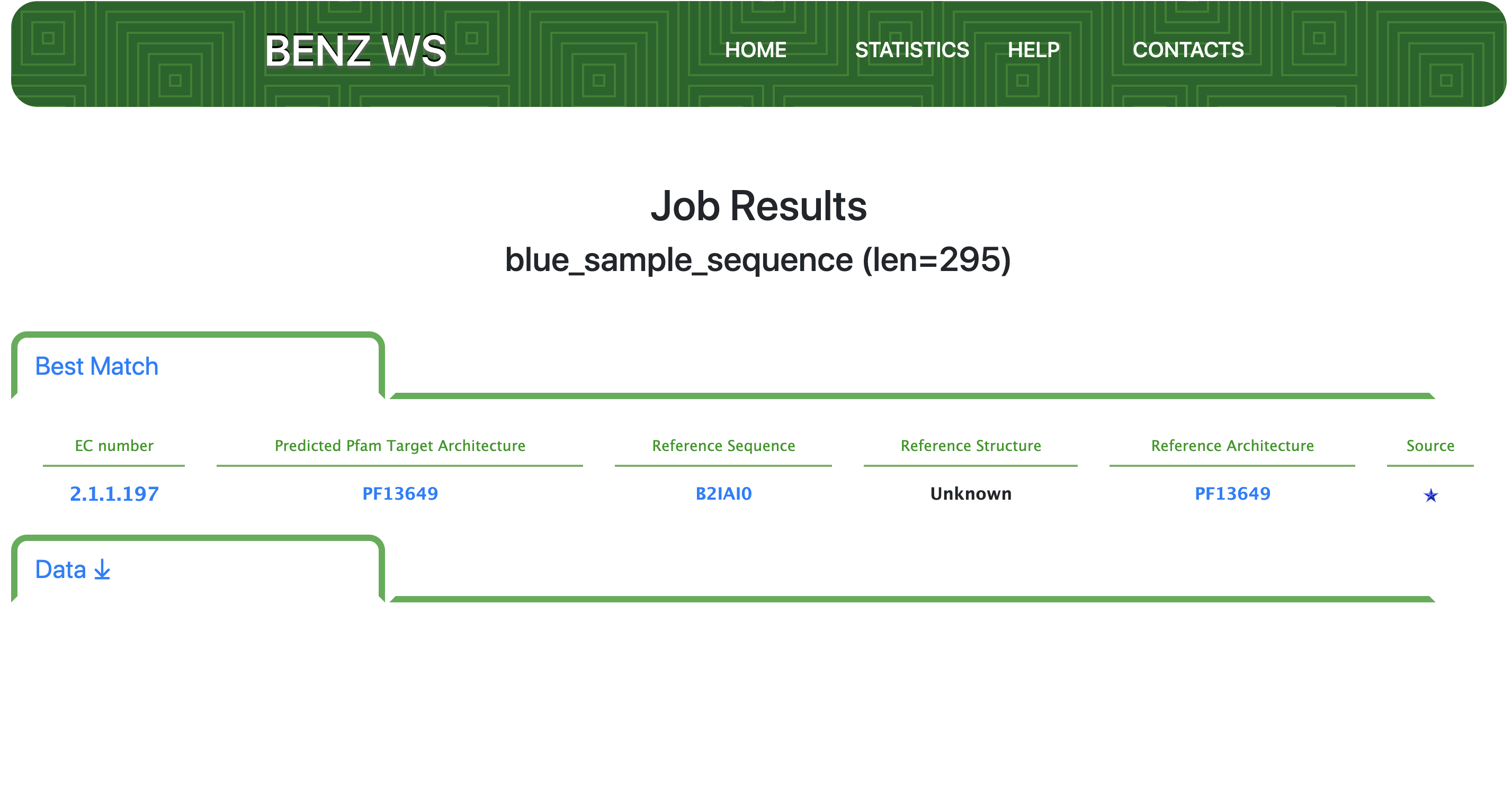
Step 2 - Results: Best Match
Results page shows on top the name (as to the FASTA header) and length of the query sequence. If BENZ-WS retains the sequence, the predicted EC number and the predicted Architecture are reported along with the reference sequence of the matched HMM (see General Overview).
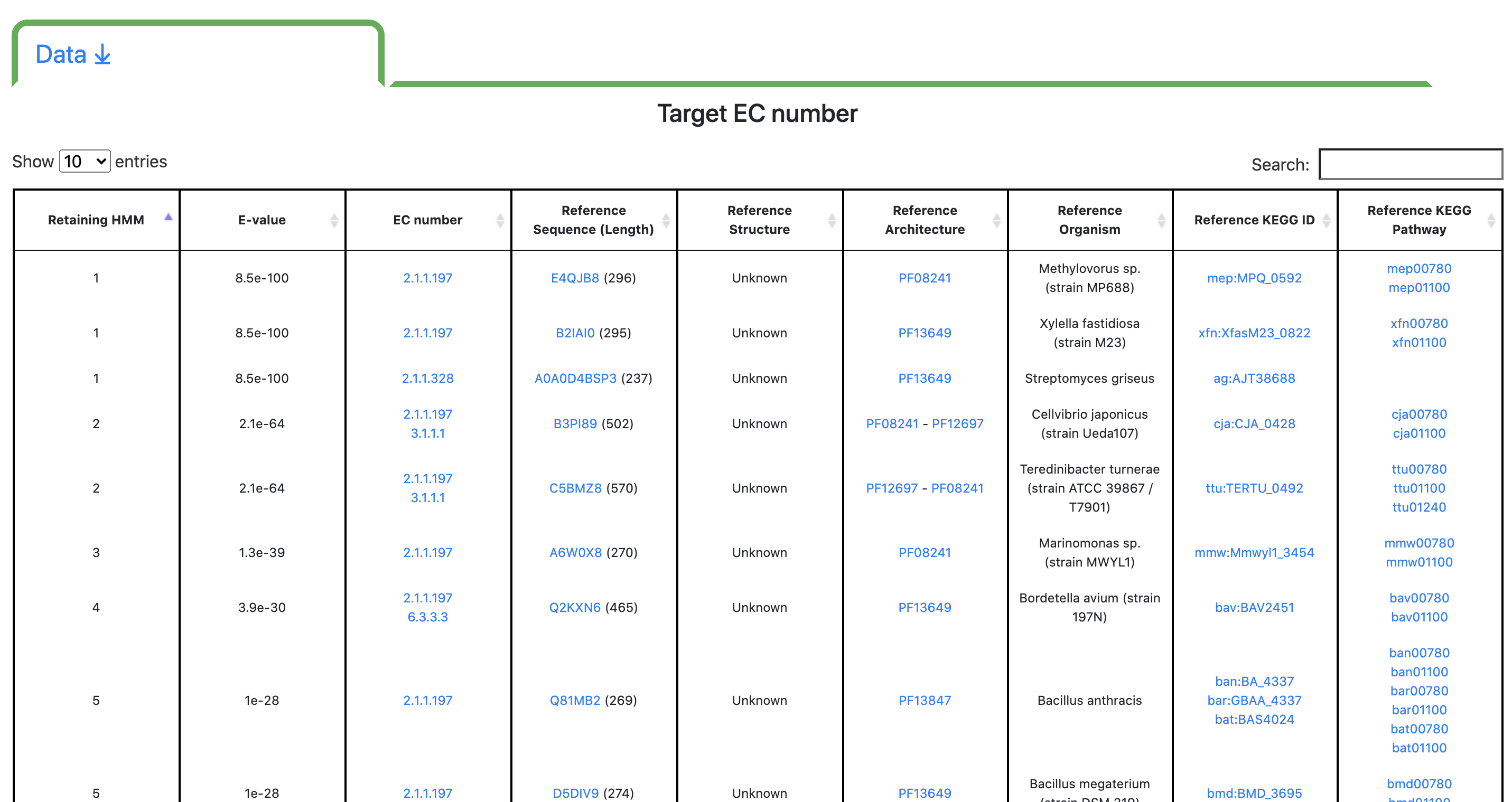
Step 3 - Results: Data
Users can display additional data by toggling the corresponding tab. The "Target EC number" table reports all the matched models sorted by E-value in ascending order. For each matched model, the associated EC number is reported as well as the reference sequence (ref seq), the reference structure (if available), the organism it comes from, the associated Kegg ID and Kegg Pathway.
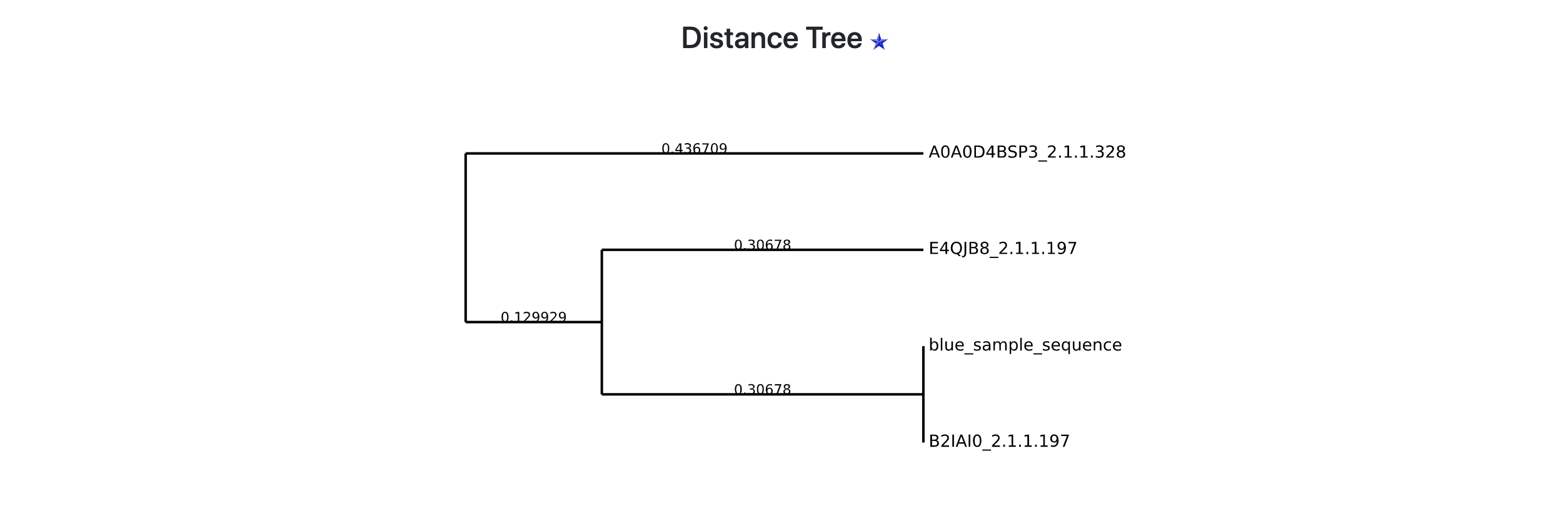
Step 4 - Results: Distance Tree (Dendrogram)
When the best HMM model is associated with more than one EC number, the most similar reference sequence is searched. The dendrogram representing the similarity relationships is displayed to users (see General Overview).
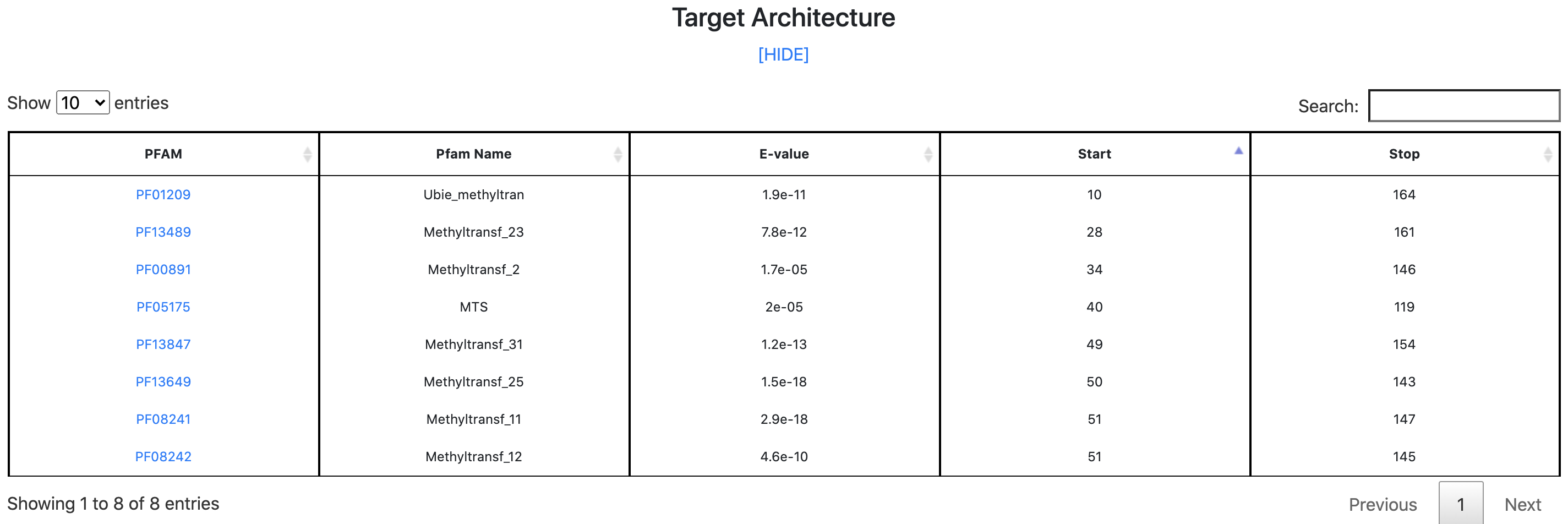
Step 5 - Results: Target Architecture
By clicking the "SHOW" button, users can display the "Target Architecture" table. This table reports all the matched PFAM domains sorted by the mapping position along the sequence.
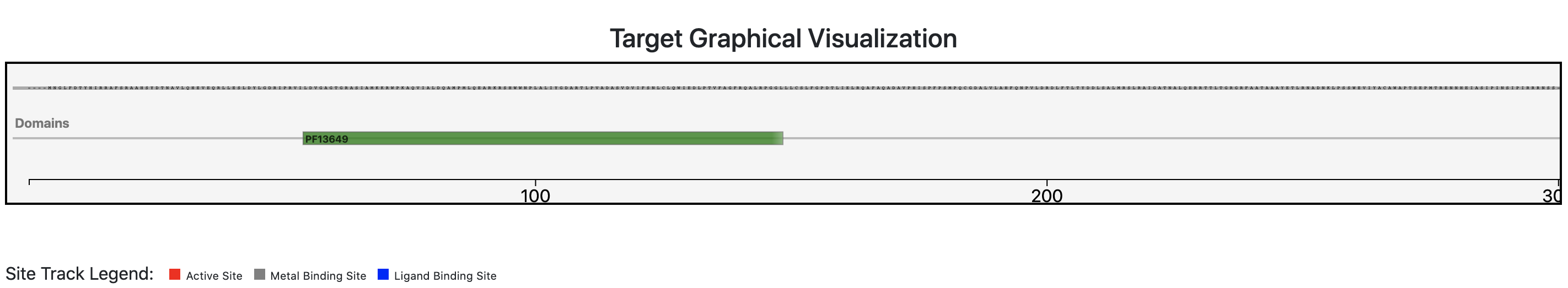
Step 6 - Results: Target Graphical Visualization
Users can investigate the predicted architecture of the query sequence by means of a protein feature viewer. Moreover, users can also check if annotated relevant sites (active, ligand binding or metal binding) are conserved in the query sequence and therefore confirm the functional prediction. Users can zoom a specific region of the query sequence by clicking and dragging the cursor over the region of interest.