Click to Go Back
General Overview
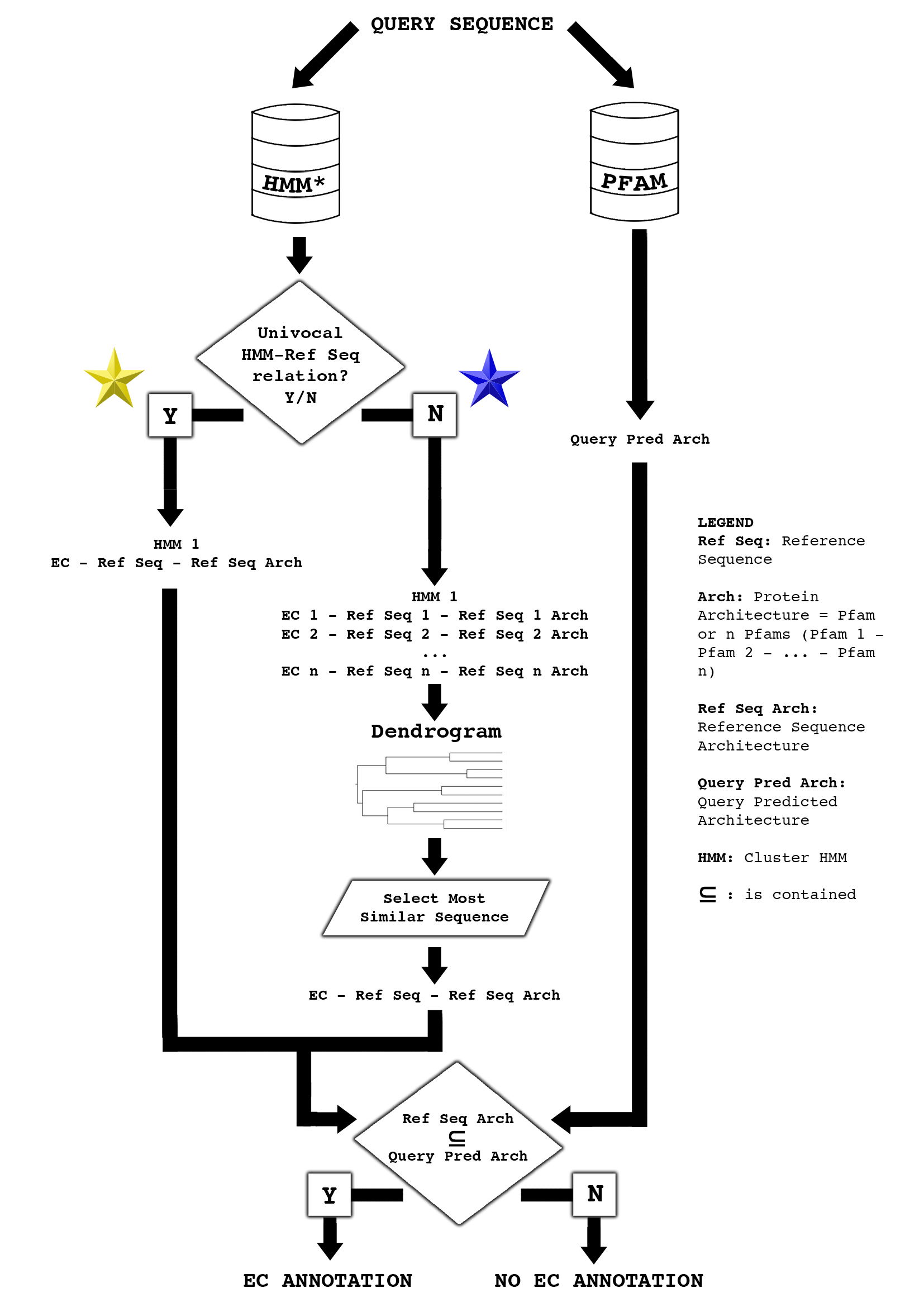
FIGURE 1. Workflow of BENZ WS. For a query sequence, in FASTA format, the annotation procedure starts with HMM filtering. If the retaining HMM is plurivocally associated to different References Sequences (blue star), a dendrogram is generated to find among the reference sequences the most similar one to the target. Otherwise (yellow star), the target is associated to the only reference. The EC number-query sequence association is then made after evaluating if the reference protein architecture (Ref Seq Arch) is contained (⊆) in that of the predicted target Pfam architecture (Query Pred Arch), focusing on Pfams carrying relevant sites. Pfams in our system are annotated when possible, with the positions of the active site, ligand binding site and metal binding site (relevant sites). A sequence feature viewer allows the user to verify whether the query sequence conserves the residues relevant to the protein catalysis for validating the transfer of annotation from the reference sequence. Links to the reference sequence UniProt/SwissProt file, structure PDB file and Pfam entries, together with KEGG identifiers and pathways are also present in the output.
The Bologna ENZyme Web Server (BENZ WS) annotates four-level Enzyme Commission numbers (EC numbers) as defined by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB). BENZ WS filters a target sequence with a combined system of HMMs and PFAMs and returns, when successful, an associated four-level EC number (FIGURE 1)
- Our procedure starts with a cluster generation based on a similarity graph created from UniProt/SwissProt release 2019_10. Each protein sequence is connected to another in the graph when they share more than 40% sequence identity over more than 90% of the sequence alignment length. After grouping sequences into clusters, we then retain 6,882 clusters containing proteins annotated with at least a four-level EC number, for a total of 5105 unique four-level EC numbers (see Statistics).
- Among the EC annotated sequences in the clusters, we define as representative the one with the best SwissProt annotation, including 70% coverage with the corresponding PDB structure (when present) and Pfam domain architecture. Via the reference sequences, clusters were then univocally or plurivocally associated with EC numbers (4,943 and 1,939 clusters were univocally and plurivocally associated to 2,795 EC and 3,118 EC numbers, respectively) (see Statistics).
- Each cluster was then modelled with a HMM and the univocal or plurivocal correspondence HMM/reference sequence/Pfam/four-level EC number was established (FIGURE 1)
- For a query sequence, in FASTA format, the annotation procedure starts with HMM filtering. If the retaining HMM is plurivocally associated to different EC numbers (Blue Star in FIGURE 1), a dendogram is generated to find among the reference sequences the most similar one to the target.
- The EC number-query sequence association is then made after evaluating the similarity of the query Pfam architecture with that of the reference protein (FIGURE 1).
- Pfams in our system are annotated, when possible, with the positions of the active site, ligand binding site and metal binding site.
- A sequence feature viewer allows the user to verify whether the query sequence conserves the residues relevant to the protein catalysis for validating the transfer of annotation from the reference sequence. Links to the reference sequence, structure and Pfam, toghether with KEGG pathways are also present in the output.